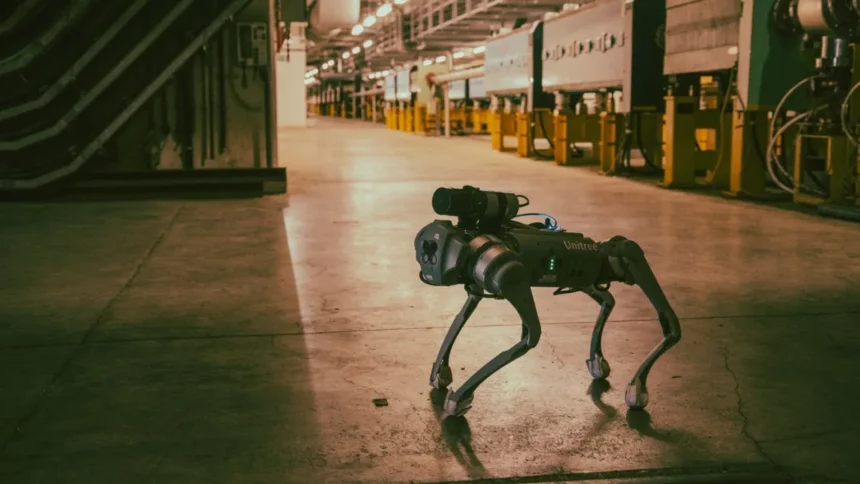
CERN, the European Organization for Nuclear Research, has introduced its latest marvel: the CERNquadbot, a versatile robot designed to navigate hazardous environments easily. This innovative creation recently underwent its first radiation protection test in CERN’s North Area, marking a significant leap in robotics technology.
Developed within CERN’s robotics hub, Building 937, the CERNquadbot boasts four legs, providing unmatched stability and maneuverability. Unlike its predecessors, which relied on wheels or tracks, this robo-dog can effortlessly traverse uneven terrains and cluttered spaces. According to Chris McGreavy, a robotics engineer at CERN, Electronics and Mechatronics (CEM) group, the robot’s unique design allows it to tackle previously challenging obstacles for humans and older robot models.
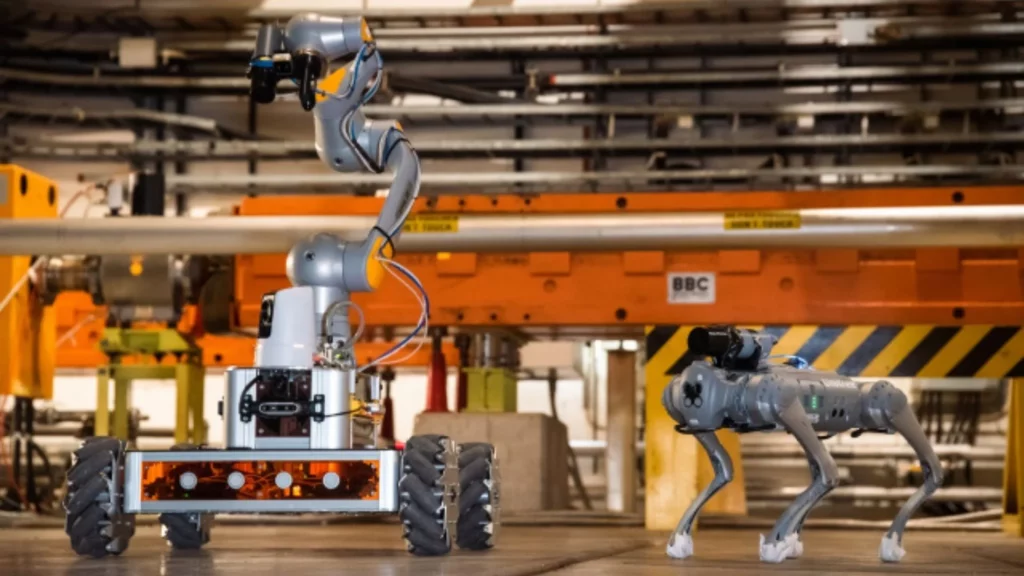
One of the standout features of the CERNquadbot is its adaptability to various environments, including complex cavern housing experiments like the ALICE detector. Equipped with advanced control algorithms, these robots can monitor environmental conditions in real time, swiftly detecting anomalies such as water or fire leaks. McGreavy emphasized their crucial role in ensuring the smooth operation of machinery within CERN’s facilities.
ALSO READ: Build Your Own Wi-fi Controlled Robot Car Using NodeMcu: A Fun and Easy DIY Project
Furthermore, integrating the CERNquadbot into CERN’s existing robotic ecosystem is a testament to the Laboratory’s commitment to innovation. This versatile robot works harmoniously with other robotic solutions, such as the Train Inspection Monorail (TIM), to enhance exploration capabilities within the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) and different challenging environments.
The introduction of the CERNquadbot reflects a broader trend in robotics, with four-legged quadruped robots gaining popularity for their agility and adaptability. These robots are invaluable in accessing hazardous areas, from offshore oil drilling sites to abandoned mining facilities. While the CERNquadbot won’t replace its wheeled or tracked counterparts entirely, it offers a unique solution to the challenges posed by radiation zones, ultimately contributing to the acceleration of scientific discovery.
ALSO READ: In Japan, security guards wear jackets with built-in AC
CERN’s unveiling of the CERNquadbot represents a significant advancement in robotics technology, promising safer and more efficient exploration of radiation zones. As this innovative robot opens doors to further advancements, the potential for prospecting within complex environments grows, ushering in a new era of discovery and innovation.









