This article will give you essential information about Amplifiers, as most electronics consist of at least one stage of Amplification. Hence, it’s used in every electrical electronics.
Here, what are Amplifiers?
The devices that higher up the input signal amplitude are known as Amplifiers.
Amplifiers work by modulating the output of the power supplied. It only speeds up other parameters, such as frequency, but the shape remains constant.
TYPES:
Amplifiers are available in different types. They can be separated or distinguished by their Amplified signals. Their functions also separate them.
CATAGORIES:
The important three Amplifiers are catalogized by their output properties.
- Voltage Amplifier
- Current Amplifier
- Power Amplifier
Let’s go into a detailed explanation.
Voltage Amplifiers:
The most commonly used Amplifiers are voltage Amplifiers. They are mostly used in every electronic appliance. Their work is to increase the signal amplitude of output voltage.
Current Amplifiers:
The working principles of current Amplifiers are changing. It works by changing or increasing the input current compared to the current waveform.
Power Amplifiers:
As it’s clear from its name, these are Introduced to increase the power. For example, if the input current and voltage value are low, these Amplifiers will Automatically increase the output current and voltage.
It doesn’t matter if the value of the input voltage or current is less; the output voltage and current result will be more incredible compared to the input.
When AC signals are applied to Amplifiers, only a few parts are Amplified because of wave Amplified. Further, Amplifiers are divided into 4 groups or classes. They are,
- Class A
- Class B
- Class AB
- Class C
Signals play an important role in the classification of Amplifiers and sub-classifications are given below
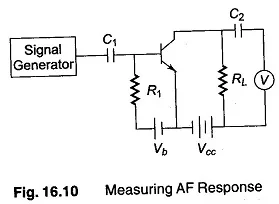
Audio Frequency Amplifiers (A.F. Amplifiers):
This type of Amplifier uses Audio Frequency, as its name indicates its qualifications. Its range is between 20Hz to 20kHz. Some high-quality Audio Amplifiers may Amplify up to 100 kHz.
The most common use of these Amplifiers is to produce loud voices, and these Audio Amplifiers are primarily used in Loudspeakers. Only some modern amplifiers are constructed based on solid-state dives; examples are transistors. At first, they are constructed as vacuum tubes.
Also read: What is Relay and How it Works?
Intermediate Frequency Amplifiers (I.F. Amplifiers):
Another important sub-division of Amplifiers is Intermediate Frequency Amplifiers, commonly used in radar, T.V., and radio.
Intermediate Frequency Amplifiers supply maximum voltage amplification to a radio, T.V., or radar signals before the video or audio information signals demodulation.
There is a change in the Frequency operating value. The received radio signal Frequency is lower than the operating frequency, but received video and audio Frequencies are higher than the operating system Frequency. So here, the electronic products choose the exact Frequency for I.F. Amplifiers operating.
Radio Frequency Amplifiers (R.F. Amplifiers):
As the name indicates, these Amplifier types maximize the power of low-frequency radio Signals. They use an Antenna as a transmitter.
Radio Frequency Amplifiers are those types of Amplifiers controlled by a tuned circuit. These circuits can be changed according to the use of this Amplifier. Generally, the input resistance is relatively low initially but increases.
The best qualification of these Amplifiers is minimum noise. Because of this qualification, they are used at first for receivers. Electronics generally produce noise in the background, but these Amplifiers keep it low as they manage low amplitude signals received from the Antenna perfectly. FET transistors can also be used at this stage.
Also read: Interfacing MFRC522 RC522 RFID Reader Module with Arduino
Ultrasonic Amplifiers:
As it’s clear from the Amplifiers name, Ultrasonic Amplifiers amplify ultrasonic waves. Their frequency range is between 20kHz to 100kHz. Its use is specific and limited. Some of the work it uses are ultrasonic cleaning, ultrasonic scanning, remote control systems, etc.
Wideband Amplifiers:
This type of Amplifier is used to amplify a band of frequency. They can amplify from D.C. to tens of MHz. They are mainly used for frequency measuring signals in a wide range accurately. Ultrasonic Amplifier’s gain is minimal because of the wide bandwidth.
Direct Coupled Amplifiers (D.C. Amplifiers):
Direct Coupled Amplifiers are used when Frequency signals are low. The Amplify process takes place in a few stages. In the first stage, the output is attached to the input of another stage. D.C. Amplifiers can also Amplify zero frequency. The most common use of D.C. Amplifiers is that it’s used in electrical systems and measuring systems.
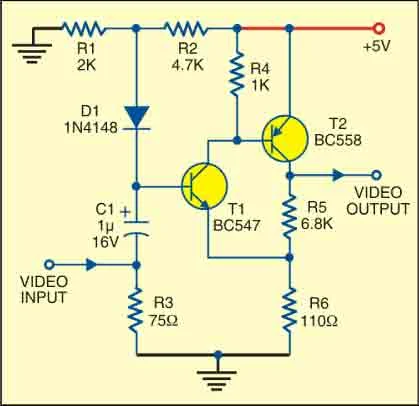
Video Amplifiers:
This type is mainly used for better video signals and high-resolution display. As we know, video signals transfer all the information about pictures in T.V. and radar systems. These are mainly used to be constructed in video equipment.
The performance of video Amplifiers depends on the use of the appliance. In T.V., its frequency varies between 0Hz to 6MHz, but in radar, it’s more comprehensive.
Video Amplifiers are mostly used to amplify received DVDs, and computers monitor signals. They are also used in small T.V. for video quality purposes such as vehicle monitors.
Buffer Amplifiers:
For electrical impedance transformation from one circuit to another, Buffer Amplifiers are mainly used. These are used for isolating circuits. They have a maximum value at the input and a low value at the output.
They can be used for Impedance-matching devices.
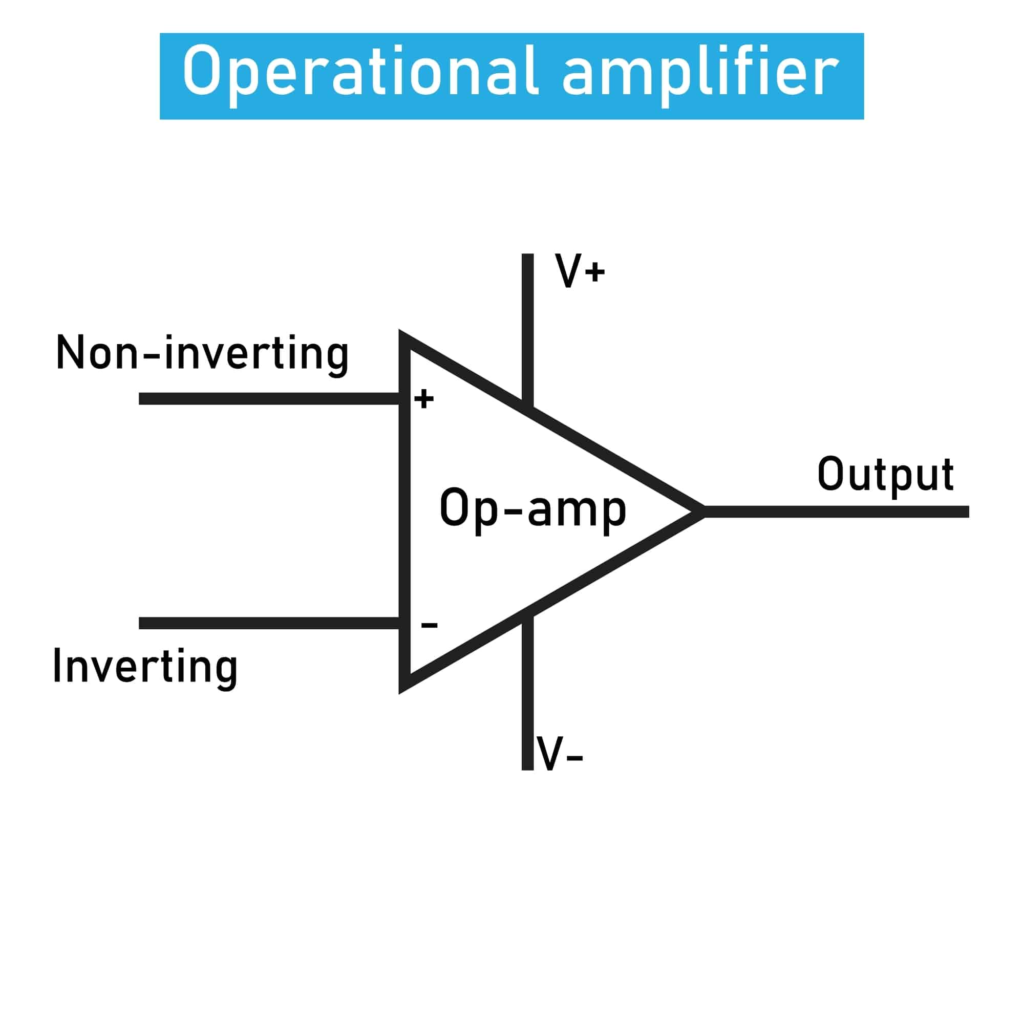
Operational Amplifiers:
These types are the most high-gain voltage Amplifiers. These are mostly used for mathematical voltage operations. Now, they are used in the shape of I.C.s. At first, they were constructed with vacuum tubes. It has two input terminals.
1: Inverting
2: Non- inverting
These can be used as inverting and non-inverting, summing, difference amplifiers, etc. The image shows an operational Amplifier.
Transistor Amplifiers:
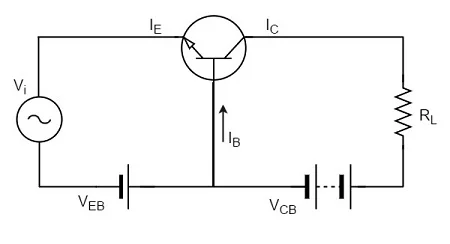
The transistor is an electronic device that also gives out functions like Amplifiers. It amplifies the voltage or current of the input signals.
Transistor types:
1) BJT (Bipolar junction transistors)
2) FET(Field Effect Transistors)
Different transistor Amplifiers configurations are given below:
1) Common Base
2) Common Emitter
3) Common Collector using BJT
Using FET, transistor amplifiers are analyzed in the following configurations.
1) Common Gate
2) Common Source
3) Common Drain
Bipolar Junction Transistors: In this transistor type, base terminals, emitter, and collector control small current values. But in Field Effect Transistors (FET), a small voltage at the gate can control the voltage at the source and drain.